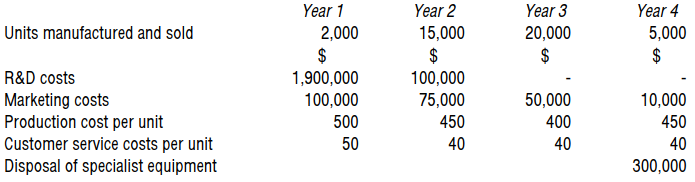快速查题-ACCA英国注册会计师试题
- 不限题型
- 不定项选择题
- 单选题
- 填空题
- 材料题
- 简答题
- 论述题
The following statements have been made about life cycle costing:
(1) Clean up costs should be included when assessing the profitability of a product
(2) It is useful for organisations that develop products with a relatively short life
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
This objective test question contains a question type which will only appear in a computer-based exam, but this question provides valuable practice for all students whichever version of the exam they are taking.
While a drag and drop style question is impossible to fully replicate within a paper based medium, some questions of this style have been included for completeness.
Which of the following are said to be benefits of lifecycle costing?
It provides the true financial cost of a product
The length of the lifecycle can be shortened
Expensive errors can be avoided in that potentially failing products can be avoided
Lower costs can be achieved earlier by designing out costs
Better selling prices can be set
Decline stages of the lifecycle can be avoided
Drag the items selected into the box below:
Moonface is developing a new piece of technology with the following expected costs.
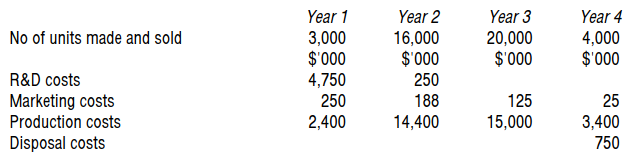
What is the life cycle cost per unit?
【论述题】
Calculate the cost per unit looking at the whole life cycle and comment on the suggested price.
The following statements relate to the justification of the use of life cycle costing:
(i) Product life cycles are becoming increasingly short. This means that the initial costs are an increasingly important component in the product’s overall costs.
(ii) Product costs are increasingly weighted to the start of a product’s life cycle, and to properly understand the profitability of a product these costs must be matched to the ultimate revenues.
(iii) The high costs of (for example) research, design and marketing in the early stages in a product’s life cycle necessitate a high initial selling price.
(iv) Traditional capital budgeting techniques do not attempt to minimise the costs or maximise the revenues over the product life cycle.
Which of these statements are substantially true?
Company B is about to being developing a new product for launch in its existing market. They have forecast sales of 20,000 units and the marketing department suggest a selling price of $43/unit. The company seeks to make a mark-up of 40% product cost. It is estimated that the lifetime costs of the product will be as follows:
(1) Design and development costs $43,000.
(2) Manufacturing costs $15/unit.
(3) Plant decommissioning costs $30,000.
The company estimates that if it were to spend an additional $15,000 on design, manufacturing costs/unit could be reduced.
What is the life cycle cost?
Life cycle costing is the profiling of cost over a product's production life
Life cycle costing is particularly useful for products with a short expected life cycle.
When are the bulk of a product's life cycle costs normally determined?
Which of the following is NOT a way of maximising return over a product life cycle?