快速查题-ACCA英国注册会计师试题
- 不限题型
- 不定项选择题
- 单选题
- 填空题
- 材料题
- 简答题
- 论述题
In which of the following circumstances are participative budgets effective?
(1) In decentralised organisations
(2) During periods of economic affluence
(3) When an organisation's different units act autonomously
One of the basic tenets of total quality management is 'get it right first time'. Is variance reporting a help or a hindrance in this respect?
Complete the table below to show a possible response to each of the traditional performance measures and a consequence of that response.
Leaf Limited has had a mixed year. Its market share has improved two percentage points to 20% but the overall market had contracted by 5% in the same period. The budgeted sales were 504,000 units and standard contribution was $12 per unit.
The sales market size variance is:
A company manufactures a specific clinical machine used in hospitals. The company holds a 2% share of the market and the total market demand has been constant at 250,000 machines for the last few years. The budgeted selling price for each machine is $10,000 and standard contribution is equivalent to 10% of the budgeted selling price.
An initial performance review of the company’s actual results showed a sales volume of 5,600 machines had been achieved. The total market demand for the machines, though, had risen to 300,000 units.
What is the market share variance for the clinical machines?
PlasBas Co uses recycled plastic to manufacture shopping baskets for local retailers. The standard price of the recycled plastic is $0.50 per kg and standard usage of recycled plastic is 0.2 kg for each basket. The budgeted production was 80,000 baskets.
Due to recent government incentives to encourage recycling, the standard price of recycled plastic was expected to reduce to $0.40 per kg. The actual price paid by the company was $0.42 per kg and 100,000 baskets were manufactured using 20,000 kg of recycled plastic.
What is the materials operational price variance?
A profit centre manager claims that the poor performance of her division is entirely due to factors outside her control. She has submitted the following table along with notes from a market expert, which she believes explains the cause of the poor performance:
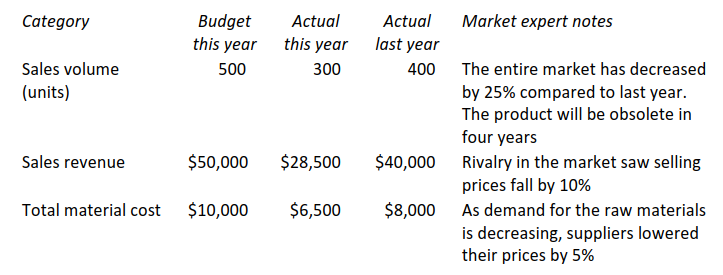 After adjusting for the external factors outside the manager’s control, in which category/categories is there evidence of poor performance?
After adjusting for the external factors outside the manager’s control, in which category/categories is there evidence of poor performance?
The following statements have been made about planning and operational variances:
(1) Planning and operational variances are calculated when it is necessary to assess a manager on results that are within his/her control.
(2) Revised standards are required because variances may arise partly due to an unrealistic budget, and not solely due to operational factors.
Which of the above statement(s) is/are true?
If a planning efficiency variance is valued at an original standard rate, the planning rate variance is valued at the original efficiency level.
A company sells a single product. Budgeted and actual sales data for the period just ended are as follows.

The budget was based on an expectation that the company would maintain its 20% share of the market. It was subsequently recognised that the actual market size, due to unforeseen changes in customer buying behaviour, was only 90,000 units. It was therefore decided to report sales volume variances as a market share variance and a market size variance.
What was the market share variance, and should this be controllable by operational sales managers?


