快速查题-ACCA英国注册会计师试题
- 不限题型
- 不定项选择题
- 单选题
- 填空题
- 材料题
- 简答题
- 论述题
The theory of constraints is an approach to production management, which aims to maximise sales revenue less:
Throughput accounting policy is to hold zero inventories throughout all operations.
This question appeared in the June 2015 exam.
The following statements have been made in relation to the concepts outlined in throughput accounting:
(1) Inventory levels should be kept to a minimum
(2) All machines within a factory should be 100% efficient, with no idle time
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
This question appeared in the June 2015 exam.
X Co uses a throughput accounting system. Details of product A, per unit, are as follows:
Selling price $320
Material costs $80
Conversion costs $60
Time on bottleneck resource 6 minutes
What is the return per hour for product A?
The following data relate to a manufacturing company. At the beginning of August there was no inventory. During August 2,000 units of product X were produced, but only 1,750 units were sold. The financial data for product X August were as follows:
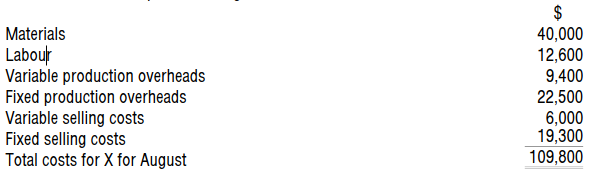
The value of inventory of X at 31 August using a throughput accounting approach is:
This objective test question contains a question type which will only appear in a computer-based exam, but this question provides valuable practice for all students whichever version of the exam they are taking.
Skye Limited has a two process environment, and details of these processes are as follows:
Process P: Each machine produces 6 units an hour and Skye has 8 machines working at 90% capacity.
Process Q: Each machine produces 9 units per hour and Skye has 6 machines working at 85% capacity.
One of Skye products is Cloud. Cloud is not particularly popular but does sell at a selling price of $20 although discounts of 15% apply. Material costs are $5 and direct labour costs are double the material cost. Cloud spends 0.2 hours in process P but 0.3 hours in process Q.
What is Cloud’s throughput per hour in its bottleneck process?
A company has recently adopted throughput accounting as a performance measuring tool. Its results for the last month are shown below.
Units produced 1,150
Units sold 800
Materials purchased 900 kg costing $13,000
Opening material inventory used 450 kg costing $7,250
Labour costs $6,900 Overheads $4,650
Sales price $35
There was no opening inventory of finished goods or closing inventory of materials.
What is the throughput accounting ratio for this product?
The following details relate to three services offered by DSF.
 All three services use the same direct labour, but in different quantities.
All three services use the same direct labour, but in different quantities.
In a period when the labour used on these services is in short supply, the most and least profitable use of the labour is:
A manufacturing company uses three processes to make its two products, X and Y. The time available on the three processes is reduced because of the need for preventative maintenance and rest breaks.
The table below details the process times per product and daily time available:
Process Hours available Hours required to make Hours required to make
per day one unit of product X one unit of product Y
1 22 1.00 0.75
2 22 0.75 1.00
3 18 1.00 0.50
Daily demand for product X and product Y is 10 units and 16 units respectively.
Which of the following will improve throughput?
The following statements have been made about throughput accounting:
A Throughput accounting considers that the only variable costs in the short run are materials and components.
B Throughput accounting considers that time at a bottleneck resource has value, not elsewhere.
C Throughput accounting views stock building as a non-value-adding activity, and therefore discourages it.
D Throughput accounting was designed as a decision-making tool for situations where there is a bottleneck in the production process.
Which ONE of the above statements is not true of throughput accounting?


