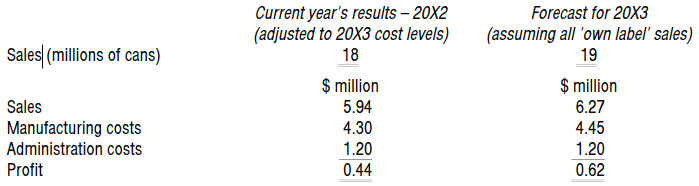快速查题-ACCA英国注册会计师试题
ACCA英国注册会计师
筛选结果
共找出2330题
- 不限题型
- 不定项选择题
- 单选题
- 填空题
- 材料题
- 简答题
- 论述题
The following question is taken from the June 2013 exam paper.
An additive time series has the following trend and seasonal variations:
Trend Y=4,000 + 6X where Y= sales in units
X is the number of quarters, with the first quarter of 2014 being 1, the second quarter of 2014 being 2 etc. Seasonal variation
Quarter 1 2 3 4
Quarterly variation (units) -4 -2 +1 +5
What is the forecast sales volume for the fourth quarter of 2015?
Quality control costs can be categorised into internal and external failure costs, inspection costs and prevention costs. In which of these four classifications would the following costs be included?
The costs of a customer service team
The cost of equipment maintenance
The cost of operating test equipment
Internal failure costs External failure costs Inspection costs Prevention costs
Cost of the a customer service team
Cost of equipment maintenance
Cost of operating test equipment
材料全屏
58
【单项选择题】
What are the equivalent units for closing work-in-progress at the end of the month?
If there had been a normal process loss of 10% of input during the month what would the value of this loss have been?
材料全屏
31
【论述题】
Prepare a contribution breakeven chart for 20X3 assuming that all sales will be 'own label'.
Prepare a contribution breakeven chart for 20X3 assuming that 50% of sales are 'own label' and 50% are of the BD brand.
Comment on the positions shown by the charts and your calculations and discuss what other factors management should consider before making a decision.
Q plc makes two products – Quone and Qutwo – from the same raw material. The selling price and cost details of these products are as shown below:
Quone Qutwo
$ $
Selling price 20.00 18.00
––––– –––––
Direct material ($2.00 per kg) 6.00 5.00
Direct labour 4.00 3.00 Variable overhead 2.00 1.50
––––– –––––
12.00 9.50
––––– –––––
Contribution per unit 8.00 8.50
The maximum demand for these products is 500 units per week for Quone, and an unlimited number of units per week for Qutwo.
What would the shadow price of these materials be if material were limited to 2,000 kgs per week?
P is considering whether to continue making a component or to buy it from an outside supplier. It uses 12,000 of the components each year.
The internal manufacturing cost comprises:
$/unit
Direct materials 3.00
Direct labour 4.00
Variable overhead 1.00
Specific fixed cost 2.50
Other fixed costs 2.00
–––––
12.50
–––––
If the direct labour were not used to manufacture the component, it would be used to increase the production of another item for which there is unlimited demand. This other item has a contribution of $10.00 per unit but requires $8.00 of labour per unit.
What is the maximum price per component, at which buying is preferable to internal manufacture?
Sales (including sales tax) amounted to $27,612.50, and purchases (excluding sales tax) amounted to $18,000.
What is the balance on the sales tax account, assuming all items are subject to sales tax at 17.5%?